Green Innovation for Food Safety: Global Trends
June 5, 2020
To mark World Food Safety Day 2020, addressing the issues of food security and sustainable development, WIPO GREEN has prepared a special feature exploring the current trends in food-related climate-friendly technology.
This year, World Food Safety Day will be celebrated under the theme Food safety, everyone's business, aimed at inspiring action for prevention and management of foodborne risks. The topics falling under the theme of food safety are closely related to sustainable agriculture and food production practices, global food security, human health, economic prosperity and sustainable development.

Food-related submissions in the WIPO GREEN database
The WIPO GREEN database is a catalogue of sustainable solutions and needs from across the world. It offers technologies from prototype to marketable products, available for license, collaboration, joint ventures, and sale. It also contains needs as defined by companies, institutions and non-governmental organizations looking for technologies to address specific environmental, food security or climate-change problems.
The WIPO GREEN database provides 425 technologies and 35 needs related to food security and food safety, coming from 31 countries. The majority of the submissions (374) are located in the Farming & Forestry category of the database, which includes farming technologies, food processing, livestock, information and communication technologies (ICT)-based solutions in farming, plant and livestock varieties, among others. Furthermore, additional food-safety related technologies can be found in the categories Water (subcategories desalinization and water treatment) and Pollution and Waste (subcategories waste disposal and food waste).
Currently, over 150 food-safety technologies and needs submitted to the database come from the USA. Chile, Japan and Kenya follow with 67, 43, and 38 submissions respectively.
Featured technology
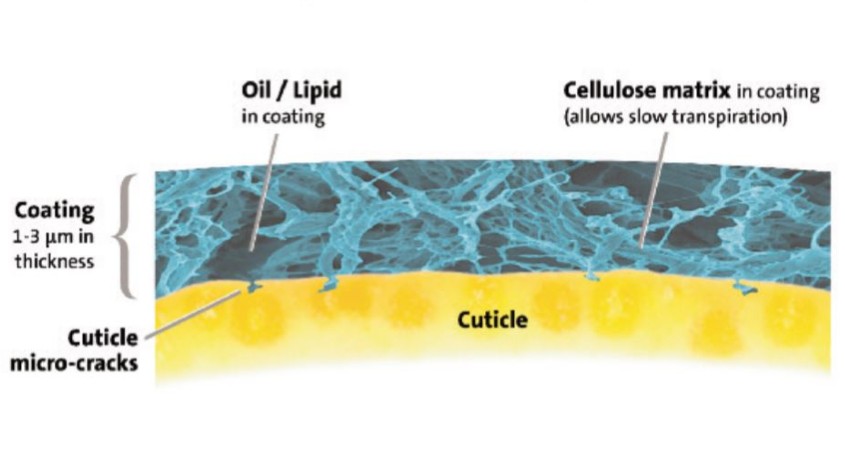
Parka, cuticle fruit care spray
Cultiva, USA
This organic edible spray is designed to complement the cuticle (a protective, film-like outer layer naturally found on fruits and leaves) of fruits and foliage of high-value crops to suppress rain-splitting, improve fruit quality and appearance, increase commercial harvest, and reduce environmental stress.
Featured TECHNOLOGY

Method for Early Detection of Salmonella Contamination in Food Samples
Purdue Research Foundation, USA
The method allows rapid concentration, retrieval and discovery of pathogens that are present in various types of food. Pathogen detection systems are necessary to prevent food-borne pathogens from spreading and harming the safety and health of a population. The present technology allows for faster process for analyzing microorganisms using enhanced microfiltration technology to identify food-borne pathogens.
Climate-smart agriculture: WIPO GREEN innovation acceleration projects
In addition to the online database, WIPO GREEN organizes innovation acceleration projects to support greentech transfer. Acceleration projects focus on a particular geographical area and technological domain, whereby providers and seekers have the opportunity to come together to fast-track the development and deployment of green technologies.
Out of the five acceleration projects that have taken place since 2015, three focused on agriculture and food security:
- Agriculture and water project in Ethiopia, Kenya and Tanzania
- Energy, clean air, water and agriculture in Cambodia, Indonesia and Philippines
- Climate Smart Agriculture in Argentina, Brazil and Chile.
The latest acceleration project in Latin America identified over 100 technologies and needs in the field of climate smart agriculture – an approach to agricultural development that conceptually links climate change and food security and aims to:
- increase agricultural productivity;
- improve resilience and reduce vulnerability to climate change and;
- reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Some of these needs can be found in our featured needs list, while the full range of technologies and needs is available on the WIPO GREEN database – accessible instantly and free of charge. Technology providers and seekers from around the world are welcome to contact the database users following a simple registration process.
Portuguese company Cubo Environmental Technologies has developed a compact, modular, containerized technology to produce safe drinking water from natural water sources, such as surface water and ground water, at an affordable price. But the firm faced a challenge: Most of the target locations for its technology do not have access to an adequate water distribution infrastructure.

In June 2017, Cubo came to an Acceleration Project event called Innovate 4 Water looking for a solution to their problem. The event brought together technology providers and entrepreneurs, investors, public sector organizations, incubators, and other stakeholders in the water sector. Among them was Susteq, a Dutch company that has developed a water payment and dispensation terminal.
Susteq’s solution sounded like a way to help Cubo deliver water to the final user by utilizing the “smart water” approach – leveraging the power of technology to integrate a payment and collection system.
At the event, Cubo’s Chief Technology Officer, Rui Brás Gomes, made contact with Susteq. After that first meeting, Rui decided to take the Cubo team to the Netherlands to visit Susteq headquarters. At the end of the trip, they established a partnership that would allow Cubo to use Susteq’s terminals in its treatment and distribution systems.
Global trends in food safety related cleantech
WIPO GREEN asked Dr. Peter Oksen, Senior Program Officer for Climate Change and Food Security at WIPO, to comment on the current trends in climate-friendly food safety innovation. A former Associate Professor in Development Studies at Roskilde University in Denmark, Peter has over 20 years of experience in socio-economic development and natural resources management, with over 15 years particularly in rural development, including agricultural development.
“Food security is one of WIPO GREEN‘s three major focus areas, encompassing technologies that promote environmentally friendly production, handling, storage, and processing of food, as well as ensuring adequate availability,” said Dr. Oksen. “We see food safety as integrated in all of these stages, and at each of them, technological innovation can contribute effective solutions.”
“Due to food safety concerns and measures taken in the retail and consumption stages, food safety is directly associated with food waste, especially in relation to fruits, vegetables, meats, and other products with relatively short shelf-life. Much food is wasted simply because it is nearing its “best before” date or because inadequate handling and storage pose a risk for food-borne illnesses.
Technological innovation is taking place in many areas that may help to address food safety. An example is advanced IT solutions improving cold chain management. Technologies such as lamps that emit electron beams to sanitize dry crops or innovative packaging methods and materials help to protect food from contamination while extending shelf life. Various technologies are also being introduced to contain or remove ethylene, a gas emitted by fruits that triggers ripening. These technologies also delay spoilage and have the potential to increase food safety and reduce food waste.
Certainly, new avenues opened by the Internet of Things, mobile applications, and blockchain technologies provide promise for significant improvements in food management efficiency thanks to more accurate and comprehensive monitoring of products in transit, cold storage, on retailer shelves, and in homes. More accurate information on the time a product spends in certain environmental conditions, its level of ripeness and on other various features contributes to the reduction in both spoilage and risks to consumer health. Omnipresent tools such as smartphones can use multi-spectral imaging technology to determine food freshness and help avoid food poisoning.
From WIPO GREEN’s perspective, we see many reasons why International Food Safety day should be celebrated, and remain optimistic with regard to the role innovation and technology can play in making the world a safer place. WIPO GREEN will soon publish two briefs on innovative technologies that help to avoid or minimize food loss and food waste; a number of the innovations mentioned here will be discussed in further detail in the forthcoming publications.”
About WIPO GREEN
WIPO GREEN is a global marketplace for sustainable technology, supporting global efforts to address climate change. Through its online database and regional activities, WIPO GREEN connects green tech seekers and providers in order to catalyze green innovation and accelerate green tech transfer and diffusion.


