Decade of Green Innovation: Celebrating 10 Years of WIPO GREEN’s Impact on Technology Exchange and Climate Solutions
November 28, 2023
Over the past decade, WIPO GREEN has successfully connected technology providers and seekers, fostering innovation and diffusion of environmentally friendly solutions worldwide, and nurturing a global ecosystem of green innovation.
WIPO GREEN’s work officially began on November 28, 2013. This year, the initiative celebrates its 10th anniversary as a pioneering marketplace for green technology. This unique online platform has played an important role in facilitating the exchange of green technologies globally.

Uniqueness of WIPO GREEN
What sets WIPO GREEN apart is its comprehensive collection of technologies at various development stages, from nascent prototypes to fully marketable products. WIPO GREEN facilitates various forms of collaboration, including licensing, joint ventures and sales, serving as the UN’s largest green technology innovation and exchange platform.
Key Achievements of WIPO GREEN
- Over 129,000 technologies, needs, and experts are listed on the WIPO GREEN database.
- Facilitating over 1,000 connections through our database, events, and projects.
- 600,000+ website visitors
- A global user base exceeding 2,500 registered users.
- Identified as a “game changing digital solution” at the UN SDG Digital Day 2023.
Main pillars of WIPO GREEN
- Technology providers: Inventors and companies can list their green technologies on WIPO GREEN, gaining global exposure and opportunities for partnerships and funding.
- Technology seekers: Organizations and investors seeking eco-friendly solutions utilize the database to find potential matches, making it a valuable resource for green tech investments.
- Partners network: WIPO GREEN’s 153 partner network includes a diverse array of stakeholders - from multinational corporations and research institutions to SMEs, fostering collaboration and partnership opportunities.

Distribution of technologies in the database
Energy sector constitutes nearly 40% of the technologies listed in the database, underscoring its pivotal role in sustainable development. Not far behind, transportation related technologies represent 18%, reflecting the innovation directed towards a category that is a major emitter of carbon. Pollution and waste technologies also contribute a considerable share at 13% of the total technologies in the database.
% of technologies in the WIPO GREEN database
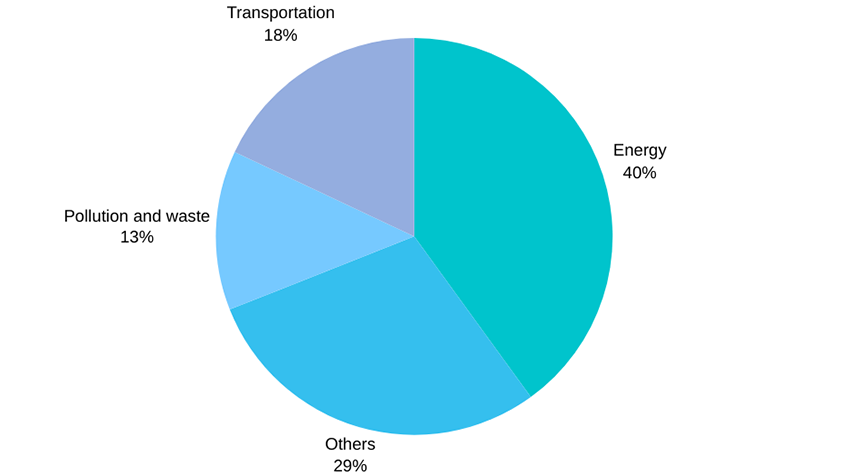
Remaining technologies are from the following sectors are relatively smaller but still represent a crucial area of focus for environmental innovation and technology: farming & forestry; water; building & construction; and product, material and processes.
Some success stories
Using innovative technology to educate future changemakers in Indonesia
Indonesia-based Green School’s Innovation Hub started looking for a way to generate drinking water for the campus, especially in the dry season. With support from a WIPO GREEN project, the Green School established collaboration with a US-originated global company, Zero Mass Water, and installed hydropanels, bringing sustainable potable water to its students. (Citation: Courtesy Green School)
Fujitsu concludes green technology licensing agreements in Japan
Fujitsu signed intellectual property licensing agreements for two technologies with Kyushu University and University of the Ryukyus. The technologies include a web app which visualizes the “natural capital” (e.g., total number of forests) of Japanese cities, wards, towns. The other was a smartphone application technology, which facilitates species identification and population prediction that supports biodiversity conservation efforts. (Citation: Fujitsu)
Leveraging micropayment technology to increase access to safe drinking water in Nigeria and Kenya
To enable access to safe drinking water, Cubo and Susteq planned a project to support 20,000 beneficiaries in Nigeria and Kenya by 2019. Both firms met at an international matchmaking event organized by WIPO GREEN. Prices were kept low by combining the low operation cost of Cubo’s equipment with the simplicity of the micropayment system developed by Susteq.(Citation: Susteq)
Managing Electric Vehicles charging stations in Beijing, China
In its recent five-year plan, Beijing proposed to have two million electric vehicles (EV) on the road by 2025. This is an ambitious goal and does not come without challenges. All these new EVs need to be recharged somewhere, creating the need to accelerate the implementation of charging facilities as well as greener sources of electricity production. Matches were made through the WIPO GREEN China Acceleration Project. (Citation: Bluetech Clean Air Alliance)
Acceleration projects
WIPO GREEN’s acceleration projects address local climate change, food security, and environmental challenges by identifying pressing needs and facilitating connections with innovative green technology solutions.
WIPO GREEN has supported technology providers and seekers to make crucial connections that can lead to the deployment, adoption and transfer of green technologies across the globe through its Acceleration Projects. Till date, WIPO GREEN has 14 such projects, which include matchmaking events, in Argentina, Brazil, Cambodia, Chile, China, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, the Philippines, Tajikistan, and Viet Nam.
These efforts have been visible in the area of climate-smart agriculture in Latin America, where a new phase of the acceleration project is making strides. Local environment challenges are being tackled by consultants in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Peru with a focus on innovative agricultural practices with funding support from the Japan Patent Office. This initiative is not only advancing sustainable agriculture in the region but also establishing vital connections between those seeking green solutions and providers. And in some cases this even includes ensuring technology adoption, like in Argentina where a peach producer in need of certified bioinputs has adopted bioinsecticide and biofertilizer technologies from a local supplier.
In Indonesia, an acceleration project on palm oil mill effluent (POME) is on-going project. Led by Winrock and backed by the Australian government, aimed to match the green technology needs of over 600 palm oil mills with sustainable solutions. The initiative has opened avenues for biogas production, showcasing how industrial by-products can be valorized for environmental benefit.
In China, collaboration between Bluetech Clean Air Alliance and the Beijing Municipal Intellectual Property Office has resulted in significant advances in contributing to reduce carbon emissions in Chinese cities. The project aligns with China’s climate commitments and has already seen the successful deployment of technologies for food waste management and intelligent energy management systems for electric vehicles.
WIPO GREEN’s matchmaking projects have a proven track record of success, as evidenced by the fruitful partnership between Green School in Indonesia and Zero Mass Water from the US, which resulted in an innovative solution for producing drinking water on a school campus using green technologies. Similar matchmaking endeavors in Cambodia, Indonesia, and the Philippines have facilitated green tech transfer, connecting technology seekers with providers.
In 2017, WIPO GREEN hosted a matchmaking event at WIPO headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, that brought together entrepreneurs and potential partners to foster innovation in the water sector. These initiatives reflect WIPO GREEN’s dedication to fostering a sustainable future through the exchange of knowledge, the formation of strategic partnerships, and the facilitation of technology transfer in green sectors.
WIPO GREEN a key digital solution to achieve UN Sustainable Development Goals
WIPO GREEN was recognized as a game-changing digital solution addressing climate change during the upcoming Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Summit at United Nations headquarters in New York on September 17th, 2023. Organized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the United Nations SDG Digital event spotlights innovative and inclusive digital solutions that advance the SDGs, like WIPO GREEN.
At the event, WIPO GREEN was highlighted as an example of how digital innovation can drive positive global change. The platform’s contribution was acknowledged in several key areas: strengthening resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters under SDG 13.1, enhancing global partnerships for sustainable development in alignment with SDG 17.16, and fostering effective cross-sector collaborations as envisioned by SDG 17.17.

“WIPO created WIPO GREEN – a free, online tech-matching platform to bring those who offer technologies to those who need these technologies, to talk to each other and form partnerships”, said Mr. Tang at the event, who commenced his speech by highlighting the importance of innovation and creativity to bring the SDGs back on track.
WIPO GREEN 10th Anniversary Symposium
On Nov. 1, 2023, the WIPO GREEN Symposium celebrated a decade of impact while also charting the path ahead to develop its new strategic plan. Marking the 10th Anniversary of WIPO GREEN, this event convened experts and stakeholders to discuss ways in which green technologies can be harnessed in the fight against climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
As WIPO GREEN steps into its next decade, we remain committed to expanding our impact and reach. We continue to strive for innovative solutions and collaborations to address the urgent environmental challenges of our time.
Understanding Green Technologies
At the heart of WIPO GREEN’s mission is the promotion of green technologies. These technologies, as outlined in Chapter 34 of Agenda 21 from the 1992 Rio United Nations Conference, are instrumental in environmental protection. They are characterized by reduced pollution, sustainable resource utilization, enhanced recycling capabilities, and improved waste management, offering a greener alternative to more polluting technologies which are in use today.


